Pneumonia
Definition of Pneumonia
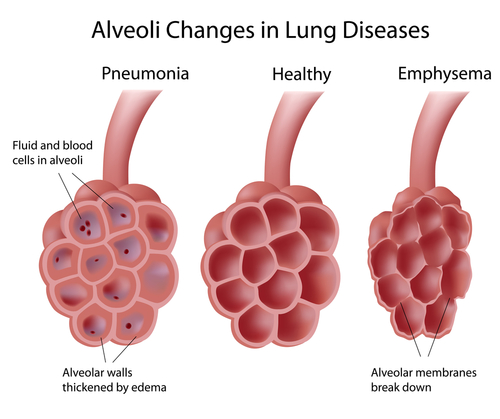
Affecting mainly the microscopic air sacs of lungs called alveoli, Pneumonia is an inflammatory disease of lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus that causes cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills and difficulty in breathing. The cause for infection includes viruses, bacteria, certain drugs and autoimmune diseases.
Cause of Pneumonia
The causes for pneumonia are many among which the most common are the bacteria and viruses in the air. Body’s immune system prevents these agents from infecting your lungs but sometimes infections do occur. Causes for pneumonia are classified on the types of germs and where they are acquired. Following are some of these types.
-
Community acquired pneumonia:
It is one of the most common types of pneumonia and is caused by following causes.
-
Bacteria: After having cold or respiratory flu you can acquire bacterial community acquired pneumonia. Usually it affects only one lung resulting in a condition called Lobar Pneumonia. The causative bacteria in most cases is Streptococcus Pneumoniae.
-
Viruses: They are the cause of pneumonia in younger children and the pneumonia is usually mild. However if caused by Influenza virus like SARS (sudden acute respiratory syndrome) it can become serious.
-
Fungi: Found in soil and bird droppings. People with underlying health problems and weak immune system are more prone to this type.
-
Hospital acquired pneumonia:
This is a type of bacterial infection that occurs when a person is hospitalized for some other conditions. This is one of the serious types as the causative bacteria are resistant to antibiotics.
-
Health care acquired pneumonia:
It is a type of bacterial infection occurring in people that live in long term care facilities like kidney dialysis centers. This type, like hospital acquired pneumonia, is also resistant to antibiotics.
-
Aspiration pneumonia:
This type occurs as a result of inhaling food, drink, vomit or saliva in one’s own lungs. Aspiration is caused by disturbance of Gag Reflex, which is caused by a brain injury, swallowing problem, or excessive use of alcohol and drugs.
Signs and Symptoms of Pneumonia
Symptoms for pneumonia are as follows.
-
 Cough
Cough -
Fever
-
Chills
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest pain
-
Increased respiration
-
Blue tinged skin
-
Decreased thirst
-
Continuous vomiting
-
Unconsciousness
-
Joint pain
-
Ear infection
Risk Factors for Pneumonia
Pneumonia can affect anyone but two age groups that are most at risk are as follows.
-
Babies and young children of 2 year age as their immune system are developing.
-
Older people of 65 years or more.
Other risk factors are as follows.
-
Chronic diseases: People with specific chronic diseases like asthma, COPD and heart diseases are more at risk of developing Pneumonia.
-
Immune system: People with factors like HIV AIDS, organ transplant, chemotherapy for cancer, or long term use of steroids have their immune systems weakened or either suppressed. This increases their risk of pneumonia.
-
Smoking destroys body’s defense against bacteria and viruses.
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
The diagnosis starts off with medical history and physical exam. This physical exam includes checking the abnormal bubbling or cracking sounds in lungs indicating the presence of thick fluids in lungs with aid of a Stethoscope. Once pneumonia is suspected following are some of the diagnostic tests.
-
Chest X-ray to check pneumonia and its location and extent.
-
Blood tests to confirm infection along with type of organism causing it.
-
Pulse oximetry to measure oxygen level of blood as pneumonia inhibits moving enough oxygen from lungs into blood stream.
-
Sputum test to pinpoint the type of infection a sample of sputum is taken after a deep cough.
Prevention from Pneumonia
To prevent pneumonia following are some tips.
-
Influenza virus is a cause for viral pneumonia. Yearly flu shot is an important protection.
-
For older people doctors recommend a one time vaccination against Pneumococcus.
-
Always use hand sanitizers and wash your hands to protect yourself against ordinary respiratory infections that often lead to pneumonia.
-
Smoking damages lungs which in turns destroys body’s immune system.
Treatment of Pneumonia
Treatment depends upon type and severity of pneumonia.
-
Antibiotics:
In case of bacterial pneumonia, best choice is antibiotics. Usually symptoms are treated in three days whereas this takes longer in smokers.
-
Antiviral medications:
Antiviral medications are prescribed to treat viral pneumonia.
-
Fever reducers:
To reduce fevers Aspirin or ibuprofen is used.
-
Cough medicine:
Coughing helps in loosening lungs and moving fluids from lungs. But to suppress coughing while resting you can use cough medicines.
.
