Duodenal Ulcer
Definition of Duodenal Ulcer
“Duodenal ulcer, sometimes called peptic ulcer, is a breach in the mucosa of duodenum (first part of small intestine).”
The appearance of the ulcer can be
-
Classic erosive
-
Concave
-
Crater like
-
Convex being the most common presentation in duodenal ulcers.
Initially they lack any visual differentiation from the surrounding tissue even in larger sizes. Convex ulcers lack any surface cratering or breaks in the mucosa.
Cause of Duodenal Ulcer
People once believed that eating spicy food was the main cause of these ulcers. Now research has shown that in addition to spicy food, there are several other causes like:
-
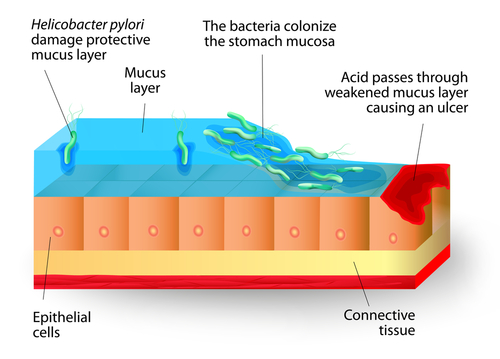
Helicobacter pylori colonize the duodenal mucosa and the immune system is unable to clear the infection. This bacterium produces some substances (mainly ammonia) that weakens the walls of duodenum and make it more susceptible to damaging effects of acid and pepsin.
-
Repeated use of aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs(NSAIDS) leave the duodenum vulnerable to harmful effects of acid and pepsin.
-
Stress no longer is considered the main cause but people with duodenal ulcers report pain when they are stressed. Same goes for smoking, alcoholism and caffeine etc.
Signs and Symptoms of Duodenal Ulcer
Common symptoms of duodenal ulcers can be
-
Heartburn
-
Chest pain
-
Loss of appetite
-
Weight loss
-
Nausea
-
Copious vomiting
-
Sensation of gnawing
-
Fullness of stomach
-
Melena (black colored stool) due to upper GIT bleeding.
-
Hematemesis (vomiting of blood) in severe cases.
Symptoms of duodenal ulcers may vary with age and severity. The timing of symptoms in relation to meal may differentiate duodenal ulcers from the stomach ulcers (gastric ulcer), as symptoms of duodenal ulcers would initially be relieved by the meals.The pyloric sphincter closes to concentrate the stomach contents, therefore acid stops reaching the duodenum. In contrast, the gastric ulcers would give epigastric pain during the meal. The pain caused by peptic ulcers can be felt anywhere from the navel up to the sternum. It may last from few minutes to several hours and it may be worse when the stomach is empty. Sometimes the pain may flare at night, and temporarily be relieved by the intake of food food or taking antacids medication.
Risk Factors for Duodenal Ulcer
Here are some of the risk factors that contribute to the formation of ulcers
-
Age and sex. It has been long believed that women and old age people are more prone to develop ulcers but recent studies have shown otherwise i.e. men are more susceptible.
-
High intake of aspirin also increases the risk.
-
High alcohol consumption
-
Caffeine overuse. People already experiencing ulcers should stay away from caffeinated drinks.
-
Cancer patients can be at high risk when undergoing radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
-
Ulcer history. If you’ve had an ulcer once, you are susceptible to having one again.
-
Skipping breakfast or more than one meal.
-
Smoking
-
Family history of ulcers
-
Blood group O
Diagnosis of Duodenal Ulcer
The diagnosis is mainly established on the symptoms and history told by the patient. Many tests are performed and are typically performed when symptoms don’t relieve after few weeks of treatment.
Usually following test are performed
-
Barium contrast x-ray
-
Endoscopy
-
Biopsy
The diagnosis of H.pylori can be made by cited below tests
-
Urea breath test.
-
Stool antigen test.
-
Measurement of antibodies level in the blood.
-
Direct Culture is difficult to do and most labs are not set up to perform H.pylori cultures.
-
Rapid urease test by direct detection of urease activity in the biopsy sample.
Prevention from Duodenal Ulcer
Steps you can take to prevent ulcers are
-
Stop using NSAIDs. You can talk with your doctor about the alternatives.
-
Do not smoke.
-
Do not drink alcohol.
-
Avoid stress.
Treatment of Duodenal Ulcer
Specific treatment for duodenal ulcer will be determined by your doctor based on
-
Your age, overall health and medical history.
-
Extent of condition.
-
Your tolerance to specific medication, therapy or procedure.
-
Expectation for the course of the treatment.
-
Your opinion or preference.
Treatments may include
-
Lifestyle changes. In the past doctors advised their patients to avoid spicy, fatty or acidic food, however a bland diet is now known to be ineffective in treating and preventing ulcers. No particular diet is helpful for most ulcer patients. People who find that certain food cause irritation should discuss the matter with their doctor. Smoking has been shown to delay ulcer healing and greater recurrence. Therefore people with ulcer are asked not to do excessive smoking.
-
Medical treatment. Doctor treat stomach and duodenal ulcer with various type of medication, including the following
-
Antibiotics kill H.pylori if it has been detected.
-
H2-blockers reduce the amount of acid in the stomach by blocking histamine,a powerful stimulant for acid secretion.
-
Mucosal protective agents shield the stomach and duodenal lining from harmful effects of acid.
-
Acid pump inhibitors completely block the stomach acid production by blocking the final step of acid secretion.
-
-
Surgery in most cases medical treatment by drugs usually heal ulcers quickly and completely. And eradication of H.pylori prevents the recurrence but sometimes surgery is necessary when patient do not respond to medication, or who develop complications.
